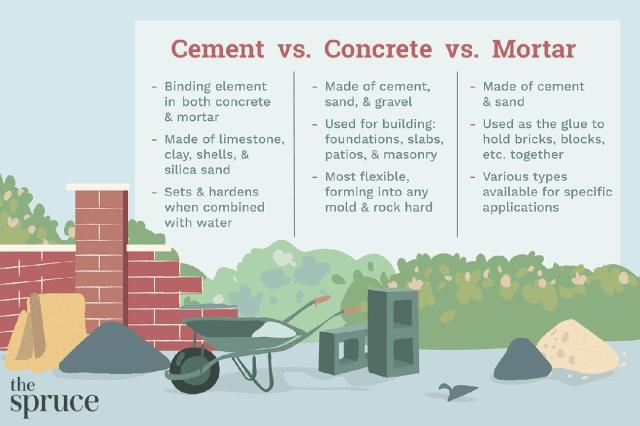
Is Concrete the Same as Cement? Myths Debunked
Concrete and cement rank among the most misunderstood terms in construction and home improvement....

Miscalculating concrete needs can waste up to 20% of your budget on a single project, turning what should be a straightforward pour into an expensive lesson. A concrete calculator prevents these costly mistakes before you start your construction project. Whether you're pouring a simple patio or building a foundation, accurate measurements make the difference between ordering exactly what you need and scrambling for emergency deliveries mid-pour. Most suppliers sell concrete by the cubic yard, which makes a concrete calculator in yards particularly useful for getting precise quantities. These tools save you time while eliminating two common headaches: emergency calls for additional concrete when you're halfway through pouring, and paying for excess material that goes to waste. You'll order precisely what your project requires, nothing more and nothing less. This guide covers how to measure properly, convert between different units, choose the right calculation method for various shapes, and decide when manual estimates work better than digital tools.
Accurate measurements form the foundation of every successful concrete project. Taking precise measurements and planning your project thoroughly saves both time and materials before you pour a single yard of concrete. Getting your measurements right the first time prevents costly mistakes and material waste.
Precise measurements determine your concrete project's success. For rectangular slabs, measure the length and width at multiple points to account for any irregularities in the project area.
Concrete thickness requirements vary by project type:
Pro Tip: For slabs on uneven ground, take measurements at several points and use the average for your calculations, or base your estimate on the deepest point to ensure adequate coverage.
For circular projects, measure the diameter (the length from one side to the other) rather than the radius when using a concrete calculator. Manual calculations require the radius (half the diameter) for the formula: Cubic yards = radius in ft × radius in ft × depth in ft × pi ÷ 27.
Most concrete calculators require measurements in feet, so converting inches to feet ensures calculation accuracy. This conversion is particularly important for depth measurements, which are often specified in inches.
Convert inches to feet by dividing the number of inches by 12:
Feet = Inches ÷ 12
|
Inches |
Feet (decimal) |
|---|---|
|
3 |
0.25 |
|
4 |
0.33 |
|
6 |
0.5 |
|
8 |
0.67 |
|
12 |
1.0 |
A typical 4-inch slab would be entered as 0.33 feet in your concrete calculator. Similarly, a 6-inch footing would be 0.5 feet. Using consistent units throughout your calculations prevents errors that could lead to ordering too much or too little concrete.
Even with precise measurements, factors beyond your control make it essential to add a waste factor. Add 10% to your final concrete volume calculation to account for:
The formula with waste factor included:
Final Volume = Calculated Volume × 1.1
If your calculations show you need 2.22 cubic yards for a patio slab, your adjusted amount with waste factor would be 2.44 cubic yards (2.22 × 1.1).
For bagged concrete, this 10% factor is sometimes automatically built into certain shortcut calculation methods. The square footage rule for 4-inch slabs: one square foot of concrete at 4 inches deep equals one 50-pound bag, 0.8 of a 60-pound bag, or 0.6 of an 80-pound bag.
Running short of concrete mid-pour can be disastrous, resulting in cold joints and a weakened structure. Ordering slightly more material creates a safety margin that prevents costly delays and potential structural issues.
Different concrete projects require specific calculation methods based on their shapes. Getting the formula right for your particular geometry ensures you order exactly what you need without shortages or waste. The calculation approach depends entirely on whether you're working with rectangles, circles, or more complex structures.
Rectangular projects offer the most straightforward concrete calculations. Multiply the length, width, and depth (all in feet) to determine concrete volume:
Cubic feet = length (ft) × width (ft) × depth (ft)
Convert to cubic yards by dividing by 27:
Cubic yards = length (ft) × width (ft) × depth (ft) ÷ 27
|
Project Type |
Length |
Width |
Depth |
Calculation |
Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Patio slab |
12 ft |
10 ft |
0.5 ft |
12×10×0.5÷27 |
2.22 cubic yards |
|
Walkway |
20 ft |
3 ft |
0.33 ft |
20×3×0.33÷27 |
0.73 cubic yards |
Footings around the perimeter often require separate calculations from the main slab. Calculate each section independently, then add them together for your total concrete volume.
Circular concrete projects use a different formula with the radius (half the diameter) and pi (3.14):
Cubic yards = radius² × depth × pi ÷ 27
A circular patio with a 10-foot diameter (5-foot radius) and 4-inch thickness (0.33 ft) needs:
Cubic yards = 5² × 0.33 × 3.14 ÷ 27 = 0.96 cubic yards
Ring-shaped projects require calculating the entire circle, then subtracting the inner circle volume. Consider a round patio with an outer radius of 6 feet and an inner radius of 4 feet:
|
Circle |
Radius |
Depth |
Calculation |
Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Outer |
6 ft |
0.33 ft |
6²×0.33×3.14÷27 |
1.39 cubic yards |
|
Inner |
4 ft |
0.33 ft |
4²×0.33×3.14÷27 |
0.62 cubic yards |
|
Total |
- |
- |
1.39-0.62 |
0.77 cubic yards |
Most concrete calculators handle the radius conversion automatically when you enter the diameter.
Stair calculations become manageable when you break the structure into rectangular sections. Think of each step as a separate rectangle when viewed from the side:
Total concrete = Section 1 + Section 2 + Section 3 + ...
The process works the same for multi-level pours with varying depths—calculate each section separately using the rectangular formula, then add all sections together.
For curbs and gutters, calculate the vertical and horizontal portions separately:
Total = Curb volume + Gutter volume
Mobile apps with AR technology can automatically calculate volumes for irregular shapes, saving significant time compared to breaking complex forms into geometric components.
Best for: Projects with irregular shapes or curves benefit most from digital measurement tools rather than manual calculations.
Choosing between manual calculations and digital tools affects both the accuracy and efficiency of your concrete project. Manual formulas work well for simple jobs, while concrete calculators offer advantages for complex projects. Not every project requires the same approach.
Manual concrete calculations make sense for specific situations:
The standard manual formula for rectangular projects remains straightforward:
Cubic yards = length (ft) × width (ft) × depth (ft) ÷ 27
For circular projects:
Cubic yards = radius² × depth × 3.14 ÷ 27
Best for: Simple projects where you need quick estimates or want to verify calculator results.
Digital concrete calculators offer several advantages over manual calculations:
|
Benefit |
Manual Calculation |
Concrete Calculator |
|---|---|---|
|
Time required |
Minutes to hours |
Seconds |
|
Accuracy level |
Moderate (human error risk) |
High (automated) |
|
Complex shapes |
Difficult |
Simple |
|
Unit conversion |
Manual |
Automatic |
|
Bag calculation |
Separate step |
Integrated |
Concrete calculators handle irregular shapes that would otherwise require complex geometry. Advanced apps use augmented reality (AR) technology to scan and measure project sites, eliminating manual measurements entirely.
Best for: Complex projects, irregular shapes, or when you need integrated material calculations.
Certain errors can lead to costly mistakes regardless of your calculation method:
Calculators reduce error risk, but they still require accurate input measurements. Double-check all dimensions before finalizing your estimate, especially for large projects where errors become expensive.
Remember that concrete comes in different strength ratings and types. Basic calculators might not account for specialized concrete needs, so consult with suppliers about specific requirements beyond simple volume calculations.
Once you've calculated the volume of concrete needed for your project, the next step involves converting that measurement into the right number of bags. Understanding bag quantities and unit conversions ensures you purchase exactly what you need.
Concrete volume comes in two primary measurements: cubic feet and cubic yards. Most concrete calculators work in cubic yards, but bagged concrete is sold by cubic feet coverage. To convert between these units:
Cubic yards = cubic feet ÷ 27
Cubic feet = cubic yards × 27
A project requiring 2.22 cubic yards equals 59.94 cubic feet (2.22 × 27). This conversion matters when purchasing bagged concrete, since packaging lists coverage in cubic feet rather than yards.
Pro Tip: One cubic yard of concrete placed at 4 inches deep covers approximately 81 square feet, equivalent to about five standard sidewalk squares.
Concrete comes in four standard bag sizes, each covering different volumes:
|
Bag Weight |
Coverage (cubic feet) |
Coverage (cubic yards) |
Bags per Pallet |
|---|---|---|---|
|
40 lb |
0.30 cu ft |
0.011 cu yards |
80 |
|
50 lb |
0.37 cu ft |
0.013 cu yards |
64 |
|
60 lb |
0.45 cu ft |
0.017 cu yards |
56 |
|
80 lb |
0.60 cu ft |
0.022 cu yards |
42 |
To determine the number of bags needed, divide your total cubic feet by the coverage per bag. If your project requires 60 cubic feet and you're using 80 lb bags:
Number of bags = 60 ÷ 0.60 = 100 bags
Calculate the exact amount, then round up to ensure an adequate supply.
For 4-inch slabs, a simple shortcut eliminates complex calculations:
One square foot of concrete at 4" depth equals:
This method includes the waste factor automatically. For an 81 square foot slab (9' × 9') at 4" deep using 80 lb bags, you'd need:
81 sq ft × 0.6 = 48.6 bags (round up to 49)
This rule of thumb works faster than converting from cubic yards, particularly for standard residential slabs. One pallet of 80 lb bags (42 bags) provides approximately one cubic yard of concrete, serving as another quick reference for larger projects.
Technology has simplified concrete calculations through specialized tools and apps that eliminate complex math and reduce errors. These digital solutions offer precision while saving time on your projects.
Several online calculators help determine concrete quantities for various projects:
|
Calculator |
Best For |
Features |
|---|---|---|
|
Sakrete Calculator |
All project types |
Product recommendations, material lists |
|
Concrete Network |
Basic calculations |
Multiple shape options, unit conversions |
|
HomeAdvisor Tools |
Cost estimation |
Volume plus price estimates |
Pro Tip: Look for calculators that automatically include the 10% waste factor to avoid underpurchasing materials.
Mobile concrete calculator apps provide flexibility during site visits. These apps allow you to:
You can make immediate adjustments without returning to the office, which helps when clients request changes during consultations.
Augmented reality technology has changed how you measure irregular concrete forms. The Sakrete App, for example, uses AR spatial technology to scan project sites and measure complex areas accurately.
These AR tools:
The app also recommends appropriate products for your specific project, removing guesswork from material selection.
Accurate concrete calculations prevent both material waste and project delays. Your choice between manual formulas and digital tools depends on your project's complexity and your comfort level with calculations.
Choose manual calculations for small, straightforward projects like post footings or simple rectangular slabs. The basic formula works well when you need quick estimates without internet access. Choose concrete calculators for complex shapes, multiple sections, or when you want built-in unit conversions and bag quantity calculations.
Project shapes determine your calculation method. Rectangular slabs need simple length-width-depth formulas, while circular structures require radius-based calculations. For multi-level pours or irregular shapes, break complex areas into manageable sections or use AR-enabled apps that scan and measure automatically.
The 10% waste factor remains essential regardless of your calculation method. This buffer accounts for spillage, uneven ground, and measurement variations that can derail a pour. For 4-inch slabs, remember the shortcut: one square foot equals one 50-pound bag, with waste already included.
Double-check your measurements before placing orders. Even the most accurate calculator produces wrong results with incorrect inputs. Take measurements at multiple points for uneven areas, and verify your unit conversions—especially when switching between inches and feet for depth calculations.
Your concrete project succeeds or fails based on preparation. Those extra minutes spent verifying calculations and measurements prevent emergency material runs and costly delays when you're ready to pour.
GET THE ESSENCE OF RELEVANT HOME
IMPROVEMENT TOPICS IN LESS THAN 5 MINUTES

Is Concrete the Same as Cement? Myths Debunked
Concrete and cement rank among the most misunderstood terms in construction and home improvement....

Fixing cracks in concrete doesn't have to be a daunting project once you understand why they occu...

Thanks for joining our homeowners’ community.
Stay tuned!
Choose the category
Choose the category